How To Read Stock
adminse
Apr 03, 2025 · 9 min read
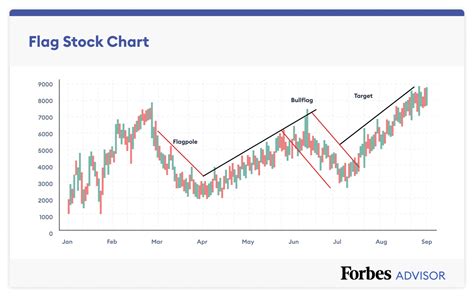
Table of Contents
How to Read Stock Charts: Unlocking the Secrets of the Market
What makes understanding stock charts a game-changer in today’s landscape?
Mastering stock chart reading is the key to unlocking informed investment decisions and navigating the complexities of the financial markets.
Editor’s Note: This comprehensive guide to reading stock charts has been published today.
Why Understanding Stock Charts Matters
In today's interconnected world, financial markets play a pivotal role in global economies. Understanding stock charts is not just a skill for seasoned investors; it's a crucial tool for anyone seeking financial literacy and potentially profitable investments. Whether you're aiming to build long-term wealth, diversify your portfolio, or simply navigate the intricacies of the stock market, the ability to interpret stock charts offers a significant advantage. It allows investors to visualize price trends, identify potential entry and exit points, and make more informed decisions based on data rather than speculation. This knowledge is applicable across various investment strategies, from long-term buy-and-hold approaches to short-term trading. The implications are far-reaching, impacting personal finances, retirement planning, and even broader economic understanding.
Overview of the Article
This article provides a comprehensive guide to interpreting stock charts, covering fundamental concepts, various chart types, technical indicators, and practical applications. Readers will gain a working knowledge of how to analyze price movements, identify trends, and assess risk, equipping them with the tools to make more informed investment choices. We will delve into the mechanics of different chart types, explain crucial technical indicators, and showcase practical examples to illustrate the concepts discussed.
Research and Effort Behind the Insights
This guide is the result of extensive research, drawing upon established financial literature, analysis of market data spanning decades, and insights from experienced financial analysts. The information presented is intended to be educational and empowering, assisting readers in developing their understanding of financial markets. However, it is crucial to remember that investing in the stock market involves inherent risks, and this article does not constitute financial advice. Independent research and consultation with a qualified financial advisor are always recommended before making any investment decisions.
Key Takeaways
| Key Concept | Description |
|---|---|
| Chart Types | Understanding Candlestick, Line, Bar charts and their applications |
| Trend Identification | Recognizing uptrends, downtrends, and sideways (consolidation) patterns |
| Support and Resistance | Identifying price levels where buying and selling pressure is expected to be strong |
| Technical Indicators | Utilizing Moving Averages, Relative Strength Index (RSI), and other indicators |
| Risk Management | Implementing strategies to limit potential losses |
| Chart Pattern Recognition | Identifying common patterns like head and shoulders, triangles, and flags |
Let’s dive deeper into the key aspects of stock chart reading, starting with the fundamental chart types and their interpretation.
Exploring the Key Aspects of Stock Chart Reading
1. Understanding Chart Types:
-
Candlestick Charts: These charts provide a rich visual representation of price action, showing the opening, closing, high, and low prices for a specific period (e.g., daily, weekly, monthly). The "body" of the candlestick represents the price range between the opening and closing prices, while the "wicks" (or shadows) extend to the high and low prices of the period. Green or white candles typically indicate a closing price higher than the opening price (bullish), while red or black candles indicate a closing price lower than the opening price (bearish).
-
Line Charts: These charts are simpler, displaying only the closing price for each period. They are useful for visualizing long-term trends but lack the detailed price information provided by candlestick charts.
-
Bar Charts: These charts visually represent the high, low, open, and close prices using vertical bars. The top of the bar shows the high, the bottom shows the low, and a short horizontal line within the bar shows the open and close prices.
2. Identifying Market Trends:
Identifying trends is crucial for making informed investment decisions. A clear upward trend (uptrend) suggests growing buyer interest, while a downward trend (downtrend) indicates increasing seller pressure. Sideways or consolidation patterns often precede significant price movements. Trendlines can be drawn to visually represent these trends, connecting a series of highs (resistance) or lows (support) to help predict future price direction.
3. Support and Resistance Levels:
Support levels represent price areas where buying pressure is anticipated to outweigh selling pressure, preventing further price declines. Resistance levels are price areas where selling pressure is expected to overcome buying pressure, hindering further price increases. These levels are often formed by previous highs and lows, providing insights into potential price reversal points. A breakout above resistance or below support can signal a significant trend change.
4. Technical Indicators:
Technical indicators are mathematical calculations based on price and volume data, providing additional insights into market trends and momentum. Some commonly used indicators include:
-
Moving Averages (MA): MAs smooth out price fluctuations, providing a clearer picture of the overall trend. Common MAs include simple moving averages (SMA) and exponential moving averages (EMA). Crossovers between different MAs (e.g., a short-term MA crossing above a long-term MA) can generate buy signals, while the opposite can signal sell signals.
-
Relative Strength Index (RSI): RSI measures the magnitude of recent price changes to evaluate overbought or oversold conditions. RSI readings above 70 are generally considered overbought, suggesting a potential price correction, while readings below 30 are often viewed as oversold, indicating potential buying opportunities.
-
MACD (Moving Average Convergence Divergence): MACD compares two moving averages to identify momentum shifts. Crossovers of the MACD line above its signal line can suggest buying opportunities, while crossovers below can suggest selling opportunities.
5. Chart Pattern Recognition:
Certain recurring patterns on stock charts can offer insights into potential future price movements. Some common chart patterns include:
-
Head and Shoulders: This pattern often suggests a trend reversal, with a distinct "head" and two "shoulders" forming a pattern that resembles a head and shoulders.
-
Triangles: Triangles are consolidation patterns characterized by converging trendlines, often indicating a period of indecision before a price breakout.
-
Flags and Pennants: These are short-term consolidation patterns that often occur within a larger trend, suggesting a temporary pause before the trend resumes.
Closing Insights
Understanding stock charts is a multifaceted skill that requires practice and experience. It's not about predicting the future with certainty, but about enhancing decision-making by analyzing past price action and identifying potential trends and patterns. By combining technical analysis with fundamental analysis (examining a company's financial health), investors can gain a comprehensive view of a stock's potential and manage risk more effectively. While the stock market is inherently unpredictable, mastering chart reading can significantly improve your ability to navigate its complexities and increase your chances of successful investing. Remember to always diversify your investments and never invest more than you can afford to lose.
Exploring the Connection Between Risk Management and Stock Chart Reading
Effective risk management is inseparable from successful stock chart reading. Understanding chart patterns, support and resistance levels, and technical indicators is crucial for determining appropriate entry and exit points, minimizing potential losses, and protecting capital. Without a well-defined risk management strategy, even the most accurate chart analysis can lead to substantial losses.
For example, placing stop-loss orders (automatic sell orders triggered when a stock price reaches a predetermined level) based on support levels identified on a chart can limit potential downside risk. Conversely, setting profit targets based on resistance levels or identified price objectives can help investors secure gains and prevent overexposure. The use of technical indicators like RSI to identify overbought or oversold conditions can further refine risk management strategies, providing additional signals for adjusting positions.
Further Analysis of Risk Management
Risk management strategies in stock trading can be categorized into several approaches:
| Risk Management Strategy | Description |
|---|---|
| Position Sizing | Determining the appropriate amount of capital to allocate to each trade. |
| Stop-Loss Orders | Setting predetermined sell orders to limit potential losses. |
| Take-Profit Orders | Setting predetermined sell orders to secure profits when a target price is reached. |
| Diversification | Spreading investments across multiple assets to reduce the impact of individual losses. |
| Hedging | Using financial instruments to offset potential losses in other investments. |
| Backtesting Trading Strategies | Evaluating the historical performance of trading strategies to assess their effectiveness. |
FAQ Section
-
Q: What is the best type of stock chart to use? A: There's no single "best" chart type. Candlestick charts offer the most comprehensive information, while line charts are best for visualizing long-term trends. The optimal choice depends on your trading style and the timeframe you're analyzing.
-
Q: How reliable are technical indicators? A: Technical indicators are tools, not guarantees. They should be used in conjunction with other forms of analysis, including fundamental analysis and an understanding of market context.
-
Q: Can I use stock chart reading for long-term investing? A: Absolutely. While many focus on short-term trading, chart analysis can also be valuable for identifying long-term trends and assessing the overall health of a stock.
-
Q: Is it necessary to use sophisticated software for chart reading? A: While advanced platforms offer many features, you can begin learning with free online charting tools. As your skills develop, you may consider investing in more advanced software.
-
Q: How long does it take to become proficient at reading stock charts? A: Proficiency requires time and practice. Consistent effort, learning from mistakes, and continuous refinement of your skills are key.
-
Q: Are there any resources available to help me learn more? A: Yes, many books, online courses, and tutorials are available. Start with the basics, practice consistently, and consider seeking mentorship from experienced traders.
Practical Tips
-
Start with the Basics: Begin by learning to interpret candlestick charts and identify basic trends.
-
Practice Regularly: Analyze historical charts of different stocks to develop your pattern recognition skills.
-
Use Multiple Indicators: Don't rely on a single indicator. Combine several indicators to confirm potential signals.
-
Manage Your Risk: Always use stop-loss orders to protect your capital and limit potential losses.
-
Develop a Trading Plan: Outline your trading strategy, including entry and exit points, risk management parameters, and position sizing.
-
Stay Updated: Market conditions change constantly. Keep abreast of economic news and events that could impact your investments.
-
Learn from Mistakes: Every trade is a learning opportunity. Analyze both successful and unsuccessful trades to refine your strategy.
-
Seek Mentorship: Consider connecting with experienced traders or joining investment communities to gain insights and learn from others.
Final Conclusion
Reading stock charts is a fundamental skill for navigating the complexities of the financial markets. While not a guaranteed path to riches, it empowers investors with the ability to make more informed decisions, manage risk effectively, and potentially enhance their investment outcomes. By understanding chart types, identifying trends, utilizing technical indicators, and employing sound risk management practices, investors can significantly improve their chances of success. Remember that continuous learning, practice, and a disciplined approach are crucial for mastering this valuable skill and achieving long-term investment success. The journey requires patience, discipline, and a commitment to continuous improvement.
Latest Posts
Latest Posts
-
What Is A Derivatives Trader
Apr 04, 2025
-
Alien Corporation Definition
Apr 04, 2025
-
How Much Does It Cost To Create A Cryptocurrency
Apr 04, 2025
-
How To Make A Bot For Trading Cryptocurrency
Apr 04, 2025
-
Aleatory Contract Definition Use In Insurance Policies
Apr 04, 2025
Related Post
Thank you for visiting our website which covers about How To Read Stock . We hope the information provided has been useful to you. Feel free to contact us if you have any questions or need further assistance. See you next time and don't miss to bookmark.