Received Pension Funds What Are The Correct Irs Forms
adminse
Apr 03, 2025 · 8 min read
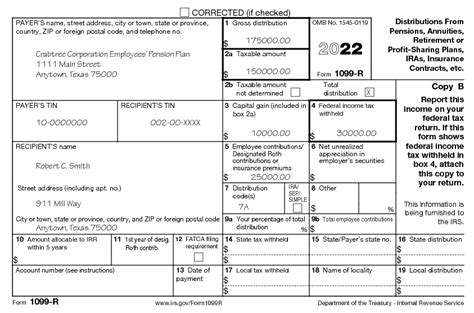
Table of Contents
Decoding Retirement: The Right IRS Forms for Your Received Pension Funds
What makes navigating IRS forms for pension income so challenging?
Understanding the correct IRS forms for your pension is crucial for accurate tax filing and avoiding penalties.
Editor’s Note: This guide on IRS forms for received pension funds has been published today to provide up-to-date information for tax season.
Why Understanding Pension Income Tax Forms Matters
Receiving a pension signifies a significant life transition, marking the culmination of years of dedicated work. However, understanding the tax implications of pension income can be complex and often confusing. Failing to accurately report your pension income can lead to significant penalties and interest from the IRS. This article aims to clarify the process, providing a comprehensive guide to the essential IRS forms involved and offering practical tips for accurate tax filing. Properly navigating these forms ensures compliance with tax laws, protects your financial well-being, and allows you to enjoy your retirement years without unnecessary financial burdens. The implications extend beyond individual taxpayers; accurate reporting contributes to the overall integrity of the tax system.
Overview of this Article
This article delves into the intricacies of reporting pension income to the IRS. We'll explore the primary forms required, delve into specific scenarios, and offer practical advice for accurate and timely tax filing. You'll gain a clear understanding of the relevant IRS forms, learn how to fill them out correctly, and discover strategies to minimize tax liabilities legally and ethically. The information provided is intended for educational purposes and should not be considered professional tax advice. Consult with a qualified tax advisor for personalized guidance based on your specific circumstances.
Research and Effort Behind the Insights
This article is the result of extensive research, drawing upon official IRS publications, tax law resources, and expert opinions from financial and legal professionals specializing in retirement planning and taxation. The information provided reflects current tax regulations and is intended to be as accurate and up-to-date as possible. However, tax laws are subject to change, so it's essential to always refer to the latest official IRS guidance.
Key Takeaways
| Key Point | Description |
|---|---|
| Primary Form: Form 1099-R | Reports the distribution of retirement plan funds, including pensions. |
| Supporting Schedules: Schedule B & 1 | Often needed to report interest income (Schedule B) and itemized deductions (Schedule 1) related to pensions. |
| Taxability of Pension Income | Only a portion of your pension income may be taxable, depending on factors like pre-tax contributions. |
| Early Withdrawal Penalties | Withdrawing funds before the designated age may incur penalties. |
| IRA Rollovers | Rolling over funds to an IRA can impact tax implications. |
Let’s dive deeper into the key aspects of reporting pension income, starting with the most important IRS form.
Form 1099-R: Your Pension Income Statement
Form 1099-R, Distributions From Pensions, Annuities, Retirement or Profit-Sharing Plans, IRAs, Insurance Contracts, etc., is the cornerstone document for reporting your pension income. This form is issued by your pension plan administrator and provides crucial details about your pension distribution, including:
- Distribution Code: This code signifies the type of distribution (e.g., early withdrawal, normal distribution, etc.), affecting how the income is taxed. Understanding this code is crucial for accurately calculating your tax liability.
- Gross Distribution: This is the total amount received from your pension.
- Taxable Amount: This represents the portion of the distribution subject to federal income tax. The difference between the gross distribution and taxable amount often reflects pre-tax contributions or tax-deferred growth.
- Payer's Name and Identification Number: This verifies the source of the distribution.
Understanding the Distribution Code on Form 1099-R
The distribution code on Form 1099-R is pivotal in determining the taxability of your pension income. Different codes reflect various circumstances, impacting how the income is reported and taxed. Common codes include:
- Code 07: This indicates a normal distribution from a qualified pension plan. The taxable amount is usually a significant portion of the distribution.
- Code 01: Represents the distribution of a lump-sum payment. Depending on the circumstances, specific rules apply to tax implications.
- Code 04: This code signifies early withdrawal, which often involves additional tax penalties.
- Code 08: Indicates distributions from a Roth IRA, generally tax-free if certain conditions are met.
Carefully examine your 1099-R for the correct code and refer to the IRS instructions for detailed explanations of each code’s implications.
Completing Your Tax Return: Beyond Form 1099-R
While Form 1099-R is central, you'll likely need additional forms to complete your tax return accurately.
Schedule B (Interest and Ordinary Dividends):
If your pension plan generated any interest income during the year, you'll need to report this on Schedule B. This is common if your pension funds are invested.
Form 1040: U.S. Individual Income Tax Return:
This is your primary tax return, where you'll consolidate all your income and deductions, including the information from Form 1099-R and other schedules.
Schedule 1 (Additional Income and Adjustments to Income):
You might use Schedule 1 to report certain deductions and adjustments that relate to your pension income, depending on your specific circumstances. This could include certain IRA contributions or other adjustments to your pension income.
Handling Early Withdrawals and Penalties:
Withdrawing funds from a pension plan before reaching the designated retirement age often results in additional taxes and penalties. Form 1099-R will reflect the amount of the penalty, which is usually 10% of the early withdrawal amount. This penalty is added to your overall tax liability. Consult a tax professional to understand your options and potential mitigation strategies.
IRA Rollovers and Their Tax Implications:
If you rolled over funds from your pension plan to an IRA, the treatment of this rollover depends on the type of IRA and your specific situation. Consult the IRS publications and consider seeking professional advice to understand the tax implications of rolling over your pension funds.
Tax Deductions Related to Pensions:
Depending on your specific circumstances, you may be entitled to certain tax deductions related to your pension plan. These might involve deductions for IRA contributions or other qualifying deductions. Consulting with a tax professional is essential to determine if you are eligible for any relevant deductions.
Exploring the Connection Between Tax Planning and Pension Income
Effective tax planning plays a vital role in maximizing your retirement income. Careful consideration of your pension income's tax implications allows for informed financial decisions that optimize your post-retirement lifestyle. Strategies such as tax-loss harvesting (if your pension funds are invested), diversification of assets, and seeking professional advice can all positively contribute to your financial well-being during retirement.
Further Analysis of Tax Implications of Different Pension Plans
Different pension plans have varied tax implications. Defined benefit plans, defined contribution plans (like 401(k)s), and individual retirement accounts (IRAs) each possess unique tax characteristics. Understanding these nuances is essential for accurate tax reporting. For example, traditional 401(k) distributions are taxed as ordinary income, whereas Roth 401(k) distributions are generally tax-free. The tax treatment of your pension will depend entirely on the specific type of plan you have.
FAQ Section:
- Q: I received multiple 1099-Rs. What should I do? A: Report each 1099-R separately on your tax return, following the instructions for each form.
- Q: What if I don't receive a 1099-R? A: Contact your pension plan administrator immediately to request the form.
- Q: Can I deduct my pension contributions? A: Generally, pension contributions made pre-tax are not deductible again on your tax return. However, certain other deductions might apply.
- Q: What if I made a mistake on my tax return? A: File an amended return using Form 1040-X as soon as possible.
- Q: I'm unsure about the taxability of my pension. What should I do? A: Consult with a qualified tax professional for personalized advice.
- Q: Where can I find more information about pension taxation? A: Consult the IRS website (irs.gov) for publications and forms related to retirement income.
Practical Tips for Accurate Pension Income Tax Reporting:
- Keep Organized Records: Maintain detailed records of all your pension-related documents, including your 1099-R, bank statements, and any supporting documentation.
- Understand Your Distribution Code: Carefully review the distribution code on your 1099-R and understand its implications.
- Use Tax Software or Professional Assistance: Utilize tax preparation software or seek professional assistance from a qualified tax advisor to ensure accuracy.
- File Your Taxes on Time: File your taxes by the annual deadline to avoid penalties.
- Review Your Tax Return Carefully: Before submitting your return, thoroughly review all the information to ensure accuracy.
- Stay Informed About Tax Laws: Stay updated on any changes to tax laws and regulations that might affect your pension income.
- Seek Professional Guidance: If you have complex tax situations or are unsure about any aspect of tax reporting, consult with a tax professional.
- Consider Tax Planning Strategies: Work with a financial advisor to develop a comprehensive tax plan for your retirement income.
Final Conclusion:
Navigating the complexities of IRS forms for received pension funds is a crucial step in ensuring accurate tax filing and managing your retirement finances effectively. By understanding the key forms, such as Form 1099-R, and utilizing available resources, retirees can confidently manage their tax obligations and enjoy a more financially secure retirement. Remember, proactive planning, proper record-keeping, and seeking professional advice when needed can significantly contribute to a smooth and stress-free tax filing experience. This empowers retirees to focus on the enjoyment of their well-deserved retirement, rather than being burdened by unnecessary financial complexities. Don't hesitate to seek professional assistance if you need help understanding the tax implications of your pension income; accurate reporting is essential for long-term financial well-being.
Latest Posts
Latest Posts
-
How To Cancel Geico Auto Insurance
Apr 04, 2025
-
How Much Does An Auto Insurance Agent Make
Apr 04, 2025
-
How Long Can My Child Stay On My Auto Insurance
Apr 04, 2025
-
Alimony Payment Definition Types Requirements
Apr 04, 2025
-
Alien Insurer Definition
Apr 04, 2025
Related Post
Thank you for visiting our website which covers about Received Pension Funds What Are The Correct Irs Forms . We hope the information provided has been useful to you. Feel free to contact us if you have any questions or need further assistance. See you next time and don't miss to bookmark.