Secular Market Definition Vs Cyclical How It Works And Example
adminse
Apr 03, 2025 · 9 min read
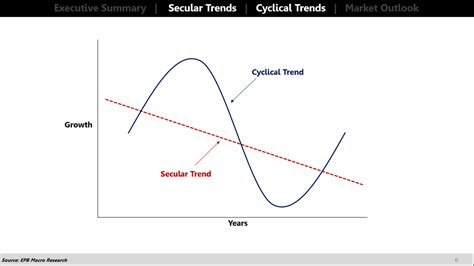
Table of Contents
Secular vs. Cyclical Markets: Unlocking the Secrets of Long-Term Investment
What distinguishes secular market trends from cyclical fluctuations, and how can this knowledge inform investment strategies?
Understanding the difference between secular and cyclical market movements is crucial for long-term investment success. Mastering this distinction allows investors to navigate market volatility and capitalize on enduring trends.
Editor’s Note: The analysis of secular and cyclical markets has been updated today to reflect the latest economic indicators and market trends.
Why Understanding Secular and Cyclical Markets Matters
The financial markets are dynamic entities, constantly fluctuating due to a multitude of factors. However, these movements aren't random; they follow discernible patterns, broadly classified as secular (long-term) and cyclical (short-term) trends. Recognizing these patterns is vital for investors seeking to maximize returns and mitigate risks. A secular bull market, for instance, can last for a decade or more, offering significant opportunities for wealth creation. Conversely, understanding a cyclical downturn allows for strategic portfolio adjustments to minimize losses. The ability to differentiate these trends helps investors avoid impulsive reactions to short-term market noise and instead focus on the bigger picture, aligning their strategies with long-term economic growth. This understanding is paramount for both individual investors and institutional portfolio managers aiming to build and preserve wealth. Ignoring this distinction can lead to poor investment decisions and suboptimal portfolio performance.
Overview of the Article
This article will delve into the core concepts of secular and cyclical markets, explaining their defining characteristics, mechanisms, and interactions. We will explore the historical context of these market behaviors, providing illustrative examples to solidify understanding. Furthermore, the article will equip readers with actionable insights to incorporate this knowledge into their investment approaches, ultimately enhancing their decision-making processes and long-term investment outcomes. Readers will gain a comprehensive grasp of the nuances between these market movements, enabling them to navigate market cycles more effectively.
Research and Effort Behind the Insights
The insights presented in this article are based on extensive research, including analysis of historical market data spanning several decades, examination of economic indicators, and review of scholarly articles and expert commentaries on market cycles. A robust methodology was employed to identify and interpret secular and cyclical market patterns, ensuring the accuracy and reliability of the information presented. The analysis draws upon established economic theories and empirical evidence, offering a data-driven perspective on this crucial aspect of investment analysis.
Key Takeaways
| Feature | Secular Market | Cyclical Market |
|---|---|---|
| Duration | 10-20+ years | Several months to a few years |
| Drivers | Technological advancements, demographic shifts, major policy changes, global economic shifts | Business cycles, investor sentiment, interest rates |
| Magnitude | Significant and long-lasting impact on prices | Moderate to significant price fluctuations |
| Predictability | Difficult to predict precisely, but patterns emerge | More predictable, but timing remains uncertain |
| Investment Strategy | Long-term investment approach; focus on fundamental analysis | Tactical asset allocation; potentially use technical analysis |
Smooth Transition to Core Discussion
Having established the importance of understanding secular and cyclical markets, let's now delve into the specifics of each, beginning with a clear definition and then progressing to illustrative examples.
Exploring the Key Aspects of Secular and Cyclical Markets
1. Defining Secular Markets:
Secular market trends represent long-term, directional movements in asset prices driven by fundamental shifts in the economy, technology, or demographics. These trends unfold over extended periods, typically spanning decades, and are far less susceptible to short-term market fluctuations. They are the underlying currents shaping the overall direction of the market. Examples include the post-World War II bull market or the tech bubble of the late 1990s and early 2000s. These trends are driven by significant, persistent forces that shape investor expectations and economic realities over many years.
2. Defining Cyclical Markets:
Cyclical market trends are shorter-term fluctuations in asset prices, characterized by periods of expansion and contraction. These cycles are typically driven by business cycles, changes in investor sentiment, interest rate adjustments, and other economic factors. These fluctuations can be quite significant within a shorter timeframe but are usually less impactful over the longer term compared to secular trends. The typical duration of a cyclical market trend ranges from months to several years. Examples include recessions, economic recoveries, and periods of high or low volatility.
3. The Interplay Between Secular and Cyclical Markets:
It’s crucial to recognize that secular and cyclical trends aren't mutually exclusive; they interact and influence one another. A cyclical downturn can occur within a secular bull market (a correction), and vice versa. Understanding this interplay is key to effective investment strategy. For example, a cyclical bear market might occur during a long-term secular bull market, presenting a buying opportunity for long-term investors. Conversely, even a robust secular bull market can experience temporary setbacks or corrections that can appear quite severe in the short-term.
4. Identifying Secular Trends:
Identifying secular trends requires a thorough analysis of fundamental economic factors, demographic shifts, technological innovations, and geopolitical events. This involves studying long-term data, understanding historical patterns, and considering the potential impact of disruptive technologies or societal changes. It's a more qualitative process involving interpreting the bigger picture rather than simply relying on short-term indicators.
5. Identifying Cyclical Trends:
Identifying cyclical trends often involves a combination of fundamental and technical analysis. Fundamental analysis focuses on macroeconomic indicators such as GDP growth, inflation, interest rates, and employment data. Technical analysis uses chart patterns and indicators to identify potential turning points in the market. Analyzing both can provide a more complete picture of the market's cyclical nature.
Closing Insights
Understanding the distinction between secular and cyclical market movements is paramount for long-term investment success. Secular trends represent the larger, long-term directional forces shaping the market, while cyclical trends represent shorter-term fluctuations. Successfully navigating both requires a combination of long-term strategic planning and short-term tactical adjustments. Ignoring the difference can lead to poor investment outcomes. Recognizing these dynamics allows investors to capitalize on sustained growth during secular bull markets and mitigate potential losses during cyclical downturns. It's not about perfectly predicting the future, but about aligning investment strategies with the underlying forces driving market movements.
Exploring the Connection Between Inflation and Secular Markets
Inflation, a sustained increase in the general price level of goods and services, significantly influences secular market trends. High inflation can erode purchasing power, impacting investor confidence and potentially triggering a bear market. However, moderate inflation is often seen as healthy for economic growth. The Federal Reserve’s role in managing inflation is critical, as its actions—raising or lowering interest rates—directly affect borrowing costs for businesses and consumers, consequently influencing investment decisions and overall market behavior. For instance, aggressive interest rate hikes aimed at curbing inflation can trigger a cyclical downturn, even within a long-term secular bull market. Conversely, periods of low inflation or deflation can contribute to a secular bull market, as investors are more confident about the future purchasing power of their investments.
Further Analysis of Inflation
| Inflation Level | Impact on Secular Market | Impact on Cyclical Market | Example |
|---|---|---|---|
| High (uncontrolled) | Potentially negative, erodes purchasing power | Increased volatility, potential bear market | Hyperinflation in Weimar Germany (1920s) |
| Moderate (controlled) | Generally positive, supports growth | Stable to moderately volatile | Post-WWII economic expansion in the US |
| Low/Deflation | Can be positive or negative; deflation can cause stagnation | Potential for slower growth, reduced volatility | Japan's lost decade (1990s-2000s) |
FAQ Section
-
Q: How long does a typical secular bull market last? A: Secular bull markets can last for 10-20 years or even longer, but their duration varies significantly.
-
Q: Can a cyclical bear market occur within a secular bull market? A: Yes, corrections and cyclical downturns are normal occurrences even during long-term upward trends.
-
Q: What are the primary drivers of secular bear markets? A: These include prolonged economic downturns, technological disruptions (leading to massive job losses), major geopolitical events, and significant policy failures.
-
Q: How can I use this knowledge to improve my investment strategy? A: By understanding both trends, you can develop a long-term investment plan that adjusts to shorter-term fluctuations.
-
Q: Are secular trends predictable? A: No, predicting the exact timing and duration of secular trends is difficult, but understanding the fundamental factors influencing them can improve your investment decisions.
-
Q: Is technical analysis useful in identifying secular trends? A: Technical analysis is primarily useful for short-term cyclical trends. For secular trends, fundamental analysis is more relevant.
Practical Tips
-
Diversify your portfolio: Spread your investments across various asset classes to reduce the impact of cyclical downturns.
-
Develop a long-term investment plan: Focus on your financial goals and don't panic-sell during cyclical corrections.
-
Stay informed: Monitor economic indicators and geopolitical events to better understand the broader market context.
-
Consider dollar-cost averaging: Invest consistently over time, regardless of market fluctuations.
-
Rebalance your portfolio: Regularly adjust your asset allocation to maintain your desired risk profile.
-
Seek professional advice: Consult a financial advisor for personalized guidance tailored to your circumstances.
-
Focus on fundamental analysis: When investing for the long term, carefully assess the underlying value of companies and assets.
-
Maintain patience and discipline: Successful long-term investing requires emotional control and a consistent approach.
Final Conclusion
Understanding the differences between secular and cyclical markets is a crucial element of effective investment strategy. While cyclical fluctuations present short-term challenges and opportunities, secular trends determine the long-term trajectory of market movements. By recognizing this distinction, investors can develop more robust and resilient portfolios, maximizing their returns over the long haul while mitigating risks associated with short-term volatility. This knowledge, coupled with a well-defined investment plan and disciplined approach, forms the bedrock for long-term investment success. Continuous learning and adaptation to evolving market dynamics are crucial in navigating the complexities of the financial landscape.
Latest Posts
Latest Posts
-
Alimony Payment Definition Types Requirements
Apr 04, 2025
-
Alien Insurer Definition
Apr 04, 2025
-
What Is Embedded Derivatives
Apr 04, 2025
-
What Is A Derivatives Trader
Apr 04, 2025
-
Alien Corporation Definition
Apr 04, 2025
Related Post
Thank you for visiting our website which covers about Secular Market Definition Vs Cyclical How It Works And Example . We hope the information provided has been useful to you. Feel free to contact us if you have any questions or need further assistance. See you next time and don't miss to bookmark.