Secure Electronic Transaction Set Definition And How It Works
adminse
Apr 03, 2025 · 8 min read
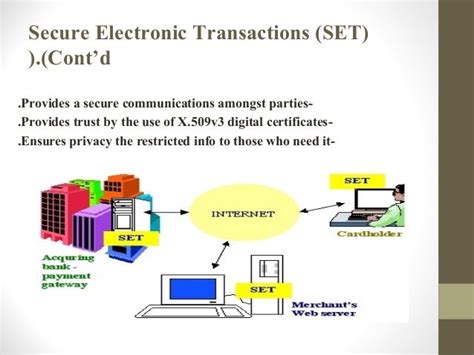
Table of Contents
Secure Electronic Transaction (SET): Definition and How It Works
What makes SET a game-changer in today’s landscape of online payments?
SET is revolutionizing online commerce by providing a robust framework for secure and trustworthy electronic transactions, fostering greater consumer confidence and driving wider adoption of digital payment systems.
Editor’s Note: Secure Electronic Transaction (SET) has been updated today to reflect its ongoing relevance and impact on the digital payments landscape.
Why SET Matters
In the ever-expanding realm of e-commerce, security remains paramount. Consumers are understandably hesitant to share sensitive financial information online unless assured of its protection. Secure Electronic Transaction (SET) emerged as a pioneering standard designed to address these concerns, providing a framework for secure credit card transactions over the internet. While newer payment technologies have gained prominence, understanding SET's principles remains crucial for grasping the evolution of online payment security. Its foundational elements continue to influence modern security protocols and best practices. Understanding SET provides valuable insights into the complexities of online payment security and the ongoing efforts to protect consumer data. The principles of SET, even if not universally implemented in its original form, serve as a cornerstone for the secure online transactions we enjoy today.
Overview of the Article
This article delves into the intricacies of SET, exploring its core components, functionality, and historical context. Readers will gain a comprehensive understanding of how SET operates, its benefits, its limitations, and its lasting influence on the digital payments landscape. We will analyze its key components, explore its practical applications, and discuss its relationship to modern payment security measures.
Research and Effort Behind the Insights
This article draws upon extensive research, including analysis of original SET specifications, examination of relevant academic papers, and review of industry reports documenting the evolution of online payment security. The information presented reflects a thorough understanding of the technology and its impact.
Key Takeaways
| Key Aspect | Description |
|---|---|
| Digital Certificates | Essential for authentication and encryption. |
| Message Digest (MD5) | Ensures message integrity. |
| Encryption Algorithms | Securely protects sensitive data during transmission. |
| Payment Applications | Facilitates interaction between merchants, consumers, and payment gateways. |
| Secure Socket Layer (SSL) | Provides secure communication channel. (Often used in conjunction with, not instead of, SET's own security.) |
Smooth Transition to Core Discussion
Let's now delve into the core components of SET, exploring its architecture and the mechanisms that ensure secure online transactions.
Exploring the Key Aspects of SET
-
SET Architecture: SET's architecture comprises several key players: the consumer, the merchant, the payment gateway, and the certification authority (CA). Each party possesses digital certificates issued by a trusted CA, verifying their identity and enabling secure communication.
-
Digital Certificates and Public Key Infrastructure (PKI): At the heart of SET lies PKI. Each participant obtains a digital certificate, a digital identity document containing their public key and other identifying information. This certificate is cryptographically signed by a trusted CA, ensuring its authenticity. The public key is used to encrypt messages, while the corresponding private key, known only to the certificate holder, decrypts them.
-
Encryption and Decryption: SET leverages robust encryption algorithms, such as RSA and DES, to protect sensitive data during transmission. The consumer's certificate is used to encrypt order information, ensuring only the merchant can decrypt it. Similarly, the merchant's certificate is used to encrypt payment information, ensuring only the consumer can decrypt it.
-
Message Integrity with MD5: To guarantee data integrity, SET employs the Message Digest 5 (MD5) algorithm. This cryptographic hash function generates a unique digital fingerprint of the message. Any alteration to the message will result in a different fingerprint, immediately revealing tampering. This ensures that the information transmitted remains unaltered during its journey across the network.
-
Payment Processing and Gateway Integration: SET integrates with payment gateways, facilitating the secure processing of credit card transactions. The payment gateway acts as an intermediary, verifying the transaction with the issuing bank and ensuring that funds are transferred securely.
-
Interoperability and Standards: SET was designed to be interoperable across different systems and platforms. This ensured that merchants and consumers could use a variety of devices and software without compromising security. However, this broad compatibility proved to be one of its challenges, as achieving universal adoption required extensive industry collaboration and agreement on technical specifications.
Closing Insights
SET, despite not achieving widespread adoption, represents a significant milestone in the evolution of online payment security. Its emphasis on digital certificates, strong encryption, and message integrity laid the groundwork for many of the security protocols employed in modern online payment systems. Although newer technologies have supplanted SET in many areas, its foundational principles remain relevant, highlighting the enduring importance of robust security in the digital world. The lessons learned from SET’s development and deployment continue to shape the design and implementation of secure online payment systems today.
Exploring the Connection Between Secure Socket Layer (SSL)/Transport Layer Security (TLS) and SET
While SET incorporated SSL (and later TLS) for secure communication, it was a separate, more comprehensive system. SSL/TLS focused on securing the communication channel, while SET focused on the broader security of the payment transaction itself, including authentication and message integrity. SET aimed to provide end-to-end security, whereas SSL/TLS only secured the connection between the client and server. Many believed that SSL/TLS was sufficient and SET’s added complexity hindered its adoption. Many modern systems now incorporate elements of both approaches, using TLS for secure communication and other mechanisms for authentication and transaction integrity.
Further Analysis of Digital Certificates
Digital certificates are the cornerstone of SET's security model. They provide a verifiable digital identity for each participant, enabling secure authentication and encryption. The trust relationship is established through the Certificate Authority (CA), which verifies the identity of certificate holders and digitally signs their certificates. Any tampering with a certificate would render its digital signature invalid, immediately alerting the system to potential fraud. The use of public and private key cryptography ensures that only the intended recipient can decrypt the encrypted information. This ensures confidentiality and authenticity of online transactions.
| Certificate Attribute | Description |
|---|---|
| Subject's Public Key | The recipient's public key, used for encryption. |
| Issuer's Information | The CA that issued the certificate. |
| Validity Period | The duration for which the certificate is valid. |
| Digital Signature | A cryptographic signature from the CA, verifying the certificate's authenticity. |
| Serial Number | A unique identifier for the certificate. |
FAQ Section
-
What is the difference between SET and other payment methods? SET is a comprehensive security protocol designed specifically for credit card transactions. Other methods, such as PayPal, offer different security features and functionalities.
-
Why didn't SET achieve widespread adoption? Its complexity, the need for widespread industry cooperation, and the emergence of simpler alternatives contributed to its limited adoption.
-
Is SET still relevant today? While not directly used in its original form, its underlying principles of digital certificates, encryption, and message integrity are crucial in modern online payment security.
-
What are the security risks associated with SET? Like any system, SET is susceptible to vulnerabilities if not properly implemented or maintained. Compromised private keys or faulty CAs pose significant risks.
-
How does SET ensure consumer privacy? By encrypting sensitive information during transmission and using digital certificates to authenticate parties, SET helps protect consumer privacy.
-
What is the future of SET's technology? While SET itself is largely obsolete, its core security principles are integrated into newer payment security systems. The concepts of digital certificates and encryption remain fundamental to online security.
Practical Tips for Enhancing Online Transaction Security
-
Use strong passwords: Employ complex and unique passwords for all online accounts.
-
Enable two-factor authentication: Add an extra layer of security to protect your accounts.
-
Keep your software updated: Regularly update your operating system and web browser to patch security vulnerabilities.
-
Shop on secure websites: Look for the padlock icon in the browser address bar, indicating an HTTPS connection.
-
Be cautious of phishing attempts: Be wary of emails or messages requesting sensitive information.
-
Monitor your accounts regularly: Check your bank and credit card statements for unauthorized activity.
-
Use reputable payment gateways: Choose well-known and trusted payment processors.
-
Use antivirus and anti-malware software: Protect your devices from malicious software that could compromise your security.
Final Conclusion
SET, while not a ubiquitous solution today, stands as a pivotal advancement in online payment security. Its contribution to the development and refinement of secure online transaction practices is undeniable. While newer technologies have overtaken SET in practical implementation, the fundamental concepts it introduced—digital certificates, encryption, message integrity—remain foundational to modern online security architecture. Understanding SET provides invaluable context for appreciating the evolution of secure digital commerce and the ongoing efforts to protect consumers in the increasingly digital marketplace. The legacy of SET's ambition and innovation continues to inspire the pursuit of ever-more robust and secure online payment systems.
Latest Posts
Latest Posts
-
How Much Does It Cost To Create A Cryptocurrency
Apr 04, 2025
-
How To Make A Bot For Trading Cryptocurrency
Apr 04, 2025
-
Aleatory Contract Definition Use In Insurance Policies
Apr 04, 2025
-
Where To Buy Tron Cryptocurrency
Apr 04, 2025
-
How To Short Cryptocurrency
Apr 04, 2025
Related Post
Thank you for visiting our website which covers about Secure Electronic Transaction Set Definition And How It Works . We hope the information provided has been useful to you. Feel free to contact us if you have any questions or need further assistance. See you next time and don't miss to bookmark.