What Is Venture Capital Vs Private Equity
adminse
Apr 03, 2025 · 8 min read
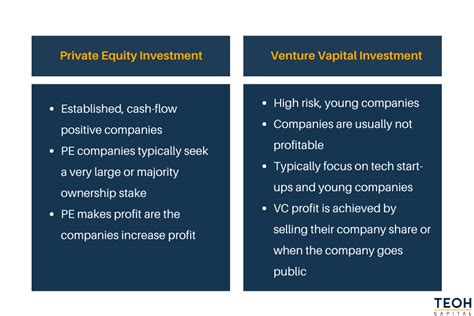
Table of Contents
Venture Capital vs. Private Equity: Unveiling the Differences
What distinguishes venture capital from private equity in today's dynamic investment landscape?
Venture capital and private equity represent distinct yet intertwined approaches to investing in companies, each with its own investment strategies, risk profiles, and target companies.
Editor’s Note: This comprehensive exploration of venture capital versus private equity has been published today, providing readers with up-to-date insights into these crucial investment strategies.
Why Venture Capital and Private Equity Matter
Understanding the nuances between venture capital and private equity is crucial for entrepreneurs seeking funding, investors looking to diversify their portfolios, and anyone interested in the dynamics of the financial markets. These investment vehicles play a significant role in fueling economic growth by providing capital to companies at various stages of development, fostering innovation, and driving job creation. Their investment decisions influence market trends and shape the future of numerous industries. Furthermore, comprehending their differences allows for informed decision-making regarding investment opportunities and risk assessment.
Overview of the Article
This article delves into the core differences between venture capital and private equity, examining their investment strategies, target companies, timelines, exit strategies, and risk profiles. Readers will gain a clear understanding of each investment class, enabling them to identify suitable investment options and appreciate the complexities of these powerful financial tools. The analysis includes real-world examples and case studies to illustrate key concepts.
Research and Effort Behind the Insights
The insights presented in this article are supported by extensive research, drawing upon reputable industry publications, academic studies, and publicly available financial data. The analysis incorporates perspectives from leading investment professionals and incorporates real-world examples of successful and unsuccessful investments to offer a balanced and comprehensive understanding.
Key Differences: Venture Capital vs. Private Equity
| Feature | Venture Capital | Private Equity |
|---|---|---|
| Investment Stage | Early-stage (seed, Series A, B, etc.) | Later-stage (buyouts, growth equity, recapitalizations) |
| Company Size | Startups, high-growth potential, often pre-revenue | Established companies, often profitable |
| Investment Size | Smaller investments, often multiple rounds | Larger investments, often single or fewer rounds |
| Investment Goal | High growth, potential for IPO or acquisition | Stable returns, operational improvements, value enhancement |
| Time Horizon | Long-term (5-10 years or more) | Medium-to-long-term (3-7 years) |
| Risk Profile | High risk, high reward | Moderate to high risk, moderate to high reward |
| Exit Strategy | IPO, acquisition | IPO, acquisition, secondary sale, recapitalization |
| Management Involvement | Active involvement, mentoring, guidance | Varying levels of involvement, often board representation |
Smooth Transition to Core Discussion:
Having established the fundamental distinctions, let's now delve deeper into the unique characteristics of each investment class.
Exploring the Key Aspects of Venture Capital and Private Equity
-
Investment Strategies: Venture capitalists (VCs) typically employ a diversified portfolio approach, investing in numerous startups across diverse sectors. They seek companies with disruptive technologies or business models possessing the potential for exponential growth. Private equity (PE) firms, on the other hand, may focus on specific industries or investment strategies (e.g., leveraged buyouts, growth equity). They often invest larger sums in fewer companies, seeking to improve operational efficiency and increase profitability.
-
Target Companies: VCs focus on early-stage companies that are often pre-revenue or have limited revenue streams. These companies typically require significant capital to fund research and development, marketing, and expansion. PE firms, conversely, target established companies with proven track records, strong management teams, and significant revenue streams. These businesses often have the potential for further growth and optimization.
-
Investment Timelines: VC investments are characterized by long timelines, often spanning 5-10 years or more. This reflects the lengthy process of nurturing startups through various growth stages until they reach a liquidity event (IPO or acquisition). PE investments typically have shorter timelines, ranging from 3-7 years, aiming for quicker returns through operational improvements and value enhancement.
-
Exit Strategies: For VCs, the most common exit strategies are initial public offerings (IPOs) and acquisitions by larger companies. PE firms also utilize IPOs and acquisitions but may also employ secondary sales to other investors or recapitalizations to restructure the company's debt.
-
Risk and Reward: VC investing is inherently high-risk, high-reward. The vast majority of startups fail, and investors face substantial losses. However, successful investments can generate extraordinary returns. PE investments typically carry a moderate to high-risk profile, with the potential for substantial returns but with lower chances of complete failure than VC investments.
-
Management Involvement: VCs play an active role in guiding and mentoring their portfolio companies, often providing valuable advice and connections. PE firms' involvement varies depending on their investment strategy and the target company's needs. Some PE firms take a more hands-on approach, while others maintain a more passive role.
Exploring the Connection Between Due Diligence and Venture Capital/Private Equity
Due diligence is paramount in both venture capital and private equity. However, the scope and depth of due diligence vary significantly depending on the investment stage and the nature of the target company.
-
VC Due Diligence: VCs conduct extensive due diligence, focusing on the team, technology, market opportunity, and competitive landscape. They also assess the company's financial projections, intellectual property, and legal compliance. Given the early-stage nature of their investments, qualitative factors often outweigh quantitative metrics.
-
PE Due Diligence: PE firms conduct comprehensive due diligence, analyzing financial statements, operational efficiency, and management capabilities. They also assess the target company's market position, competitive advantages, and regulatory environment. Quantitative analysis often plays a more significant role compared to VC due diligence due to the availability of historical financial data.
Further Analysis of Due Diligence
| Aspect | Venture Capital Due Diligence | Private Equity Due Diligence |
|---|---|---|
| Focus | Team, technology, market, scalability, qualitative factors | Financial performance, operational efficiency, management, quantitative factors |
| Data Sources | Market research, industry experts, product demonstrations, projections | Financial statements, operational data, industry benchmarks, historical performance |
| Methods | Interviews, site visits, technical assessments, legal reviews | Financial modeling, valuation analysis, operational reviews, legal reviews |
| Challenges | Limited historical data, predicting future performance, assessing technological risk | Identifying hidden liabilities, assessing management competency, ensuring accurate financial data |
FAQ Section
-
Q: What is the difference in the typical fund size between VC and PE firms? A: VC funds are generally smaller than PE funds, reflecting the smaller investment sizes in their portfolio companies.
-
Q: Which investment strategy is riskier, VC or PE? A: VC investing is generally considered riskier due to the early-stage nature of the investments and the higher probability of failure.
-
Q: How do VCs and PE firms generate returns? A: VCs generate returns primarily through IPOs or acquisitions of their portfolio companies. PE firms generate returns through a combination of operational improvements, increased profitability, and eventual sale or IPO.
-
Q: What are the key characteristics of a successful VC or PE investment? A: Strong management team, disruptive technology or business model, large market opportunity, and defensible competitive advantage.
-
Q: What are some common mistakes made by VC and PE investors? A: Overpaying for assets, underestimating execution risk, failing to adequately assess management, and neglecting market dynamics.
-
Q: How do VCs and PEs differ in their approach to portfolio company management? A: VCs often take a more hands-on approach, providing mentorship and guidance. PEs may vary in their level of involvement, ranging from active operational improvement to more passive oversight.
Practical Tips
-
Understand your risk tolerance: Assess your risk appetite before investing in either VC or PE.
-
Conduct thorough due diligence: Carefully evaluate investment opportunities, considering both quantitative and qualitative factors.
-
Diversify your portfolio: Spread your investments across various companies and sectors to mitigate risk.
-
Develop a long-term perspective: VC and PE investments require a long-term horizon, often spanning several years.
-
Seek professional advice: Consult with experienced financial advisors to guide your investment decisions.
-
Network with industry professionals: Building relationships with VCs and PE professionals can provide valuable insights and opportunities.
-
Stay updated on market trends: Keep abreast of industry developments and emerging investment themes.
-
Assess management capabilities: Evaluate the management team's experience, competence, and vision.
Final Conclusion
Venture capital and private equity represent distinct investment approaches, each catering to specific company stages and investor profiles. While both seek to generate substantial returns, their strategies, risk profiles, and timelines differ significantly. Understanding these differences is crucial for entrepreneurs seeking funding, investors navigating the investment landscape, and anyone seeking a deeper understanding of the forces shaping the global economy. The insights provided in this article serve as a foundation for making informed decisions and effectively participating in these dynamic investment markets. Further exploration into specific industry sectors and investment strategies will provide even more granular insights into the intricacies of venture capital and private equity.
Latest Posts
Latest Posts
-
Alternative Documentation Definition
Apr 04, 2025
-
Alternative Dispute Resolution Adr Definition And Meaning
Apr 04, 2025
-
Alternative Depreciation System Ads Definition Uses Vs Gds
Apr 04, 2025
-
How To Trade Derivatives
Apr 04, 2025
-
How To Remember Derivatives Of Trig Functions
Apr 04, 2025
Related Post
Thank you for visiting our website which covers about What Is Venture Capital Vs Private Equity . We hope the information provided has been useful to you. Feel free to contact us if you have any questions or need further assistance. See you next time and don't miss to bookmark.