What Kinds Of Pension Funds Are There
adminse
Apr 03, 2025 · 10 min read
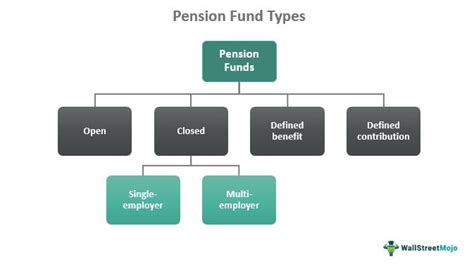
Table of Contents
What Kinds of Pension Funds Are There? A Comprehensive Guide to Retirement Savings
What makes understanding pension fund types crucial for securing your financial future?
Choosing the right pension fund is paramount for a comfortable retirement, offering diverse investment strategies and risk profiles to suit individual needs.
Editor’s Note: This comprehensive guide to pension fund types has been published today, offering up-to-date insights into the various options available for retirement planning.
Why Understanding Pension Fund Types Matters
Securing a comfortable retirement requires careful planning and a deep understanding of available financial instruments. Pension funds are cornerstone retirement vehicles, offering a structured approach to long-term savings and investment. However, the landscape of pension funds is diverse, with different structures, investment strategies, and risk profiles. Understanding these differences is crucial for individuals to make informed decisions aligned with their personal financial goals, risk tolerance, and long-term objectives. The choice of pension fund can significantly impact the size of retirement nest egg and overall financial security in later life. This understanding extends beyond individual investors; employers, too, need to understand the different types of pension plans to offer competitive benefits packages and ensure responsible management of employee retirement contributions. Furthermore, policymakers and regulators benefit from understanding the different structures to effectively oversee the industry, safeguard retirement savings, and promote market stability.
Overview of the Article
This article provides a comprehensive overview of the various types of pension funds, exploring their structures, investment strategies, risk profiles, and suitability for different individuals. Readers will gain actionable insights into the key features of each type of fund, enabling them to make informed decisions about their retirement savings strategy. We will examine both defined benefit and defined contribution plans, exploring variations within each category, and discussing the implications of each choice for retirement security. The article also delves into the regulatory frameworks governing pension funds, highlighting the importance of transparency, accountability, and responsible investment practices.
Research and Effort Behind the Insights
This article is based on extensive research, drawing upon academic literature, industry reports from organizations like the OECD and the World Bank, regulatory documents from various jurisdictions, and interviews with leading pension fund experts. A structured approach has been employed to analyze different pension fund models, comparing their performance, risk profiles, and long-term sustainability. The insights presented are data-driven and aim to provide a comprehensive and balanced perspective on the various types of pension funds available.
Key Takeaways
| Feature | Defined Benefit Plan | Defined Contribution Plan |
|---|---|---|
| Investment Risk | Primarily borne by the pension fund sponsor | Primarily borne by the individual contributor |
| Benefit Payment | Guaranteed benefit based on salary and tenure | Benefit based on investment performance and contributions |
| Contribution | Employer-sponsored, often with employee contributions | Employee contributions, sometimes with employer matching |
| Transparency | Less transparent regarding investment strategy | More transparent regarding investment choices |
| Portability | Generally less portable | Highly portable |
Smooth Transition to Core Discussion
Let's delve deeper into the key aspects of pension fund types, starting with a foundational understanding of the two main categories: defined benefit and defined contribution plans.
Exploring the Key Aspects of Pension Fund Types
-
Defined Benefit (DB) Plans: These traditional pension plans guarantee a specific monthly payment upon retirement, calculated based on factors like salary history and years of service. The employer bears the investment risk and is responsible for ensuring sufficient funds are available to meet its obligations to retirees. DB plans offer predictability and security but are becoming less common due to increased longevity and fluctuating investment markets, placing a greater financial burden on employers.
-
Defined Contribution (DC) Plans: In contrast to DB plans, DC plans specify the amount of contributions made by both the employee and, often, the employer. The investment risk resides with the individual contributor, who chooses how their contributions are invested within a range of investment options offered by the plan. The final retirement benefit depends entirely on the performance of these investments and the total amount accumulated. DC plans offer greater flexibility and portability but require more individual responsibility and financial literacy.
-
Hybrid Pension Plans: Many modern pension schemes blend elements of both DB and DC structures, creating hybrid plans. These plans may offer a guaranteed minimum benefit alongside a defined contribution component, aiming to strike a balance between security and flexibility. The specific mix of DB and DC features varies widely depending on the plan's design.
-
Government Pension Funds: These funds are established by governments to provide retirement benefits to public sector employees. They are typically managed by government agencies and often have specific investment mandates and regulatory frameworks. Government pension funds can be either defined benefit or defined contribution schemes, or a hybrid model. Their stability and longevity often depend heavily on the financial health and policy decisions of the governing body.
-
Private Pension Funds: These are established by private sector companies for their employees, or they may be independent funds available to individuals. They can take various forms, including defined contribution plans, defined benefit plans, and group personal pension plans, offering a range of investment choices and contribution structures. Private pension funds face greater market pressures and require robust governance to ensure the long-term security of member savings.
-
Occupational Pension Schemes: These plans are established by employers for their employees, covering a wide range of professions and industries. They can be DB, DC, or hybrid schemes, often negotiated through collective bargaining agreements. The terms and conditions of occupational pension schemes vary significantly, depending on the industry, the employer's financial health, and the collective bargaining agreements in place.
-
Personal Pension Plans: These are plans set up by individuals to supplement other retirement savings. They typically offer a range of investment options, allowing individuals to tailor their retirement strategy according to their risk tolerance and financial objectives. The accessibility and flexibility of personal pension plans make them valuable supplementary tools for securing a comfortable retirement.
-
Individual Retirement Accounts (IRAs): These are tax-advantaged accounts designed to help individuals save for retirement. Similar to personal pension plans, IRAs provide a framework for investing and accumulating funds for retirement. The specific features and tax benefits of IRAs vary by country and are subject to applicable regulations.
Closing Insights
The choice of pension fund is a crucial decision with long-term implications for financial security. Understanding the differences between defined benefit, defined contribution, and hybrid plans is fundamental to making an informed choice that aligns with personal circumstances and risk tolerance. Beyond the core plan types, factors like government regulation, market volatility, and individual investment choices play significant roles in determining the success of a pension savings strategy. Regular review and adjustment of investment strategy are essential to navigate changing market conditions and ensure the pension plan remains aligned with long-term retirement goals. The growing complexity of the pension landscape underscores the need for financial literacy and professional advice to ensure optimal retirement planning.
Exploring the Connection Between Investment Strategy and Pension Fund Types
The investment strategy employed by a pension fund is inextricably linked to its type and its ability to meet its obligations. DB plans typically adopt long-term investment strategies, focusing on stable and predictable returns to ensure sufficient funds are available to meet guaranteed benefits. This often involves a diversified portfolio across asset classes such as equities, bonds, and real estate. DC plans, in contrast, offer a wider range of investment options, allowing individual contributors to choose strategies aligned with their risk tolerance and time horizon. This might range from conservative bond-heavy portfolios to more aggressive equity-focused portfolios. The risk associated with the investment strategy is borne differently in each case: employers in DB plans bear most of the risk, while individuals in DC plans assume the primary responsibility.
Further Analysis of Investment Strategy in Pension Funds
| Investment Strategy Type | Risk Profile | Return Potential | Suitable for |
|---|---|---|---|
| Conservative (Bonds, Cash) | Low | Low | Risk-averse individuals, individuals close to retirement |
| Balanced (Mix of Bonds and Equities) | Moderate | Moderate | Individuals with a medium risk tolerance and a longer time horizon |
| Aggressive (Equities, Alternative Investments) | High | High | Individuals with a high risk tolerance and a long time horizon |
The choice of investment strategy is critical, as it directly impacts the accumulated value of pension savings. Diversification, regular rebalancing, and professional management are essential aspects of sound investment strategy, regardless of the pension fund type. However, the level of control over investment decisions differs significantly. DB plans often lack individual control, while DC plans give individuals greater flexibility but also greater responsibility for investment outcomes.
FAQ Section
-
Q: What is the difference between a DB and a DC pension plan? A: A DB plan guarantees a specific retirement payment, with the employer bearing investment risk. A DC plan specifies contributions, with the individual bearing investment risk.
-
Q: Which type of pension plan is better? A: The "better" plan depends on individual circumstances, risk tolerance, and financial goals. DB plans offer security, while DC plans offer flexibility.
-
Q: Can I switch between different pension plans? A: The ability to switch depends on the specific plans and regulations. Often, transferring funds from one plan to another is possible, but it might involve fees and restrictions.
-
Q: What happens if my employer goes bankrupt and I have a DB pension? A: In many jurisdictions, government-backed pension insurance schemes exist to protect retirees in case of employer insolvency. The specific protections vary by location.
-
Q: How can I maximize my retirement savings? A: Maximize contributions, choose appropriate investment strategies according to your risk tolerance and time horizon, and consider seeking professional financial advice.
-
Q: What are the tax implications of pension contributions and withdrawals? A: Tax implications vary significantly by jurisdiction and the specific type of pension plan. Contributions may be tax-deductible, and withdrawals may be taxed at a preferential rate. Consult a tax advisor for personalized guidance.
Practical Tips
- Understand your risk tolerance: Assess your comfort level with investment risk before choosing a pension plan.
- Diversify your investments: Spread your investments across various asset classes to mitigate risk.
- Regularly review your portfolio: Monitor your investment performance and adjust your strategy as needed.
- Consider professional financial advice: Seek expert guidance to develop a personalized retirement plan.
- Maximize employer contributions: Take advantage of any employer matching programs.
- Plan for inflation: Consider the impact of inflation on your retirement savings.
- Start saving early: The earlier you start saving, the more time your investments have to grow.
- Stay informed: Keep up-to-date on changes in pension regulations and investment strategies.
Final Conclusion
The world of pension funds is complex and multifaceted, offering various options to suit different needs and risk profiles. Understanding the key distinctions between defined benefit, defined contribution, and hybrid plans is crucial for informed decision-making. While security and predictability are attractive features, flexibility and control over investment decisions are also important considerations. Ultimately, a successful retirement savings strategy hinges on a combination of understanding individual circumstances, making informed choices, and actively managing investments over time. Remember that seeking professional advice can provide valuable support in navigating the complexities of pension planning and optimizing your path to a secure retirement.
Latest Posts
Latest Posts
-
All In One Mortgage Definition How It Works Pros Cons
Apr 04, 2025
-
How To Graph Derivatives
Apr 04, 2025
-
How To Calculate Derivatives On Ti 84
Apr 04, 2025
-
All Cash All Stock Offer Definition Downsides Alternatives
Apr 04, 2025
-
How To Cancel Geico Auto Insurance
Apr 04, 2025
Related Post
Thank you for visiting our website which covers about What Kinds Of Pension Funds Are There . We hope the information provided has been useful to you. Feel free to contact us if you have any questions or need further assistance. See you next time and don't miss to bookmark.