Return On Equity Roe Formula Made Easy
adminse
Apr 03, 2025 · 8 min read
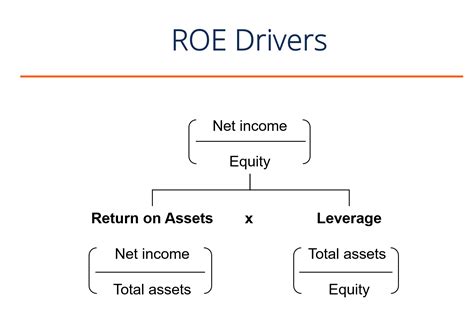
Table of Contents
Return on Equity (ROE) Formula Made Easy: Unlocking Profitability Insights
What makes understanding the Return on Equity (ROE) formula a crucial skill for investors and business owners?
Mastering the ROE formula unlocks the secrets to a company's profitability and empowers informed decision-making.
Editor’s Note: This comprehensive guide to the Return on Equity (ROE) formula has been published today.
Why Return on Equity Matters
Return on Equity (ROE) is a cornerstone financial metric that measures a company's profitability relative to its shareholders' equity. It essentially answers the crucial question: How effectively is a company using its shareholders' investment to generate profits? A high ROE indicates efficient capital utilization and strong profitability, while a low ROE may signal potential problems requiring attention. Understanding ROE is crucial for investors evaluating potential investments, for business owners monitoring performance, and for financial analysts assessing a company's financial health. It provides a standardized measure to compare profitability across different companies, even those with varying sizes and capital structures. ROE is widely used in financial modeling, valuation, and performance benchmarking.
Overview of This Article
This article will provide a detailed, step-by-step explanation of the ROE formula, its components, and how to interpret the results. We'll explore various methods of calculating ROE, address common misconceptions, and delve into how different factors influence ROE. Furthermore, we will examine how ROE relates to other key financial ratios and its importance in strategic decision-making. Readers will gain a comprehensive understanding of ROE and its practical applications.
Research and Effort Behind the Insights
This article is the result of extensive research, drawing upon established accounting principles, financial analysis textbooks, and industry best practices. We have utilized real-world examples to illustrate the concepts and ensure practical application.
Key Takeaways
| Key Aspect | Description |
|---|---|
| ROE Formula | Net Income / Shareholders' Equity |
| Components of ROE | Net Income, Shareholders' Equity |
| ROE Interpretation | Higher ROE indicates greater profitability and efficiency; Lower ROE may indicate potential issues. |
| ROE & Other Financial Ratios | ROE's relationship with Profit Margin, Asset Turnover, and Financial Leverage |
| Factors Affecting ROE | Profitability, efficiency, financial leverage, and accounting practices |
| Using ROE in Investment Analysis | A critical metric for evaluating investment opportunities and comparing company performance. |
Let’s dive deeper into the key aspects of the ROE formula, starting with its foundational elements and practical applications.
Exploring the Key Aspects of the ROE Formula
-
Understanding Net Income: Net income is the bottom line figure on a company's income statement. It represents the company's profits after all expenses, including taxes and interest, have been deducted from revenues. It's crucial to ensure that the net income figure used in the ROE calculation is consistent with the chosen period for shareholders' equity.
-
Defining Shareholders' Equity: Shareholders' equity represents the residual interest in the assets of a company after deducting all liabilities. It's essentially the net asset value attributable to the owners. Shareholders' equity is calculated as: Assets - Liabilities. For ROE calculation, the average shareholders' equity over a period (e.g., a year) is generally used to smooth out fluctuations. This average is calculated as (Beginning Shareholders' Equity + Ending Shareholders' Equity) / 2.
-
The ROE Calculation: The fundamental ROE formula is simple:
ROE = Net Income / Shareholders' Equity
For example, if a company has a net income of $10 million and shareholders' equity of $50 million, its ROE would be 20% ($10 million / $50 million = 0.20 or 20%).
-
Analyzing ROE Trends: A single ROE figure provides limited insight. Analyzing trends in ROE over time, comparing it to industry averages, and examining the underlying components contributing to ROE changes is crucial for a comprehensive understanding. A declining ROE, despite stable or growing net income, might indicate increased capital investment diluting returns.
-
DuPont Analysis: Deconstructing ROE: The DuPont analysis breaks down ROE into its constituent parts, providing a deeper understanding of the drivers of profitability. This expanded formula reveals how profit margins, asset turnover, and financial leverage interact to influence ROE. The standard DuPont formula is:
ROE = (Net Income / Sales) * (Sales / Total Assets) * (Total Assets / Shareholders' Equity)
This can be further simplified into:
ROE = Net Profit Margin * Asset Turnover * Equity Multiplier
- Net Profit Margin: Measures how much profit a company generates for each dollar of sales.
- Asset Turnover: Measures how efficiently a company utilizes its assets to generate sales.
- Equity Multiplier: Measures the extent to which a company uses debt financing (higher multiplier signifies higher debt).
Closing Insights
The ROE formula, while seemingly simple, is a powerful tool for understanding a company's profitability and efficiency. Its application extends beyond simply calculating a percentage; it facilitates deep dives into a company's financial health and informs strategic decisions. By analyzing the components of ROE and leveraging the DuPont analysis, investors and business owners can identify areas for improvement and make informed choices about investments and resource allocation. Understanding ROE is not just about numbers; it's about gaining actionable insights into a company's performance and future potential. Consistent monitoring and analysis of ROE are essential for sustainable growth and profitability.
Exploring the Connection Between Profit Margin and ROE
Profit margin is a critical component of the DuPont analysis and significantly impacts ROE. A higher profit margin directly contributes to a higher ROE, assuming other factors remain constant. A company with high sales but low profit margins will have a lower ROE than a company with lower sales but higher profit margins. Profit margin is calculated as: Net Income / Revenue. Analyzing the relationship between profit margin and ROE helps pinpoint areas where cost reduction or revenue enhancement strategies can boost profitability and improve ROE. For example, a company might analyze its cost structure, pricing strategies, and operational efficiency to improve its profit margin and, consequently, its ROE.
Further Analysis of Profit Margin
| Factor Affecting Profit Margin | Impact on Profit Margin | Impact on ROE (ceteris paribus) | Example |
|---|---|---|---|
| Increased Sales Prices | Increase | Increase | Implementing premium pricing for unique products |
| Reduced Cost of Goods Sold | Increase | Increase | Streamlining production processes |
| Lower Operating Expenses | Increase | Increase | Implementing cost-saving measures |
| Increased Revenue | Increase | Increase | Expanding into new markets |
| Increased Competition | Decrease | Decrease | Facing price wars with competitors |
| Economic Downturn | Decrease | Decrease | Reduced consumer spending |
Analyzing the connection between profit margin and ROE reveals how critical efficient cost management and revenue generation are to a company's overall financial health.
FAQ Section
-
Q: What is the ideal ROE? A: There's no universally ideal ROE. A "good" ROE depends on the industry, the company's risk profile, and its growth stage. Comparing a company's ROE to its industry average provides a more meaningful benchmark.
-
Q: How does debt affect ROE? A: High levels of debt can artificially inflate ROE. While increasing leverage initially boosts ROE, it also increases financial risk. Sustainable growth requires a balanced approach to financing.
-
Q: Can a company have a negative ROE? A: Yes, a negative ROE indicates that the company is losing money. This can be due to various factors, such as poor management, intense competition, or economic downturn.
-
Q: How often should ROE be calculated? A: ROE should be calculated periodically, typically quarterly or annually, to monitor performance trends.
-
Q: What are some limitations of ROE? A: ROE doesn't consider the size or growth of a company. It can also be affected by accounting choices, making comparisons between companies challenging.
-
Q: How does ROE relate to other key financial ratios? A: ROE is closely related to other profitability ratios like Return on Assets (ROA) and Return on Capital Employed (ROCE). Understanding these interrelationships provides a holistic view of a company's financial performance.
Practical Tips for Improving ROE
-
Boost Sales: Implement effective marketing strategies, expand into new markets, or develop new products to increase revenue.
-
Control Costs: Analyze expenses carefully to identify areas for improvement, such as streamlining operations or negotiating better deals with suppliers.
-
Enhance Operational Efficiency: Improve productivity through automation, process optimization, or employee training.
-
Manage Inventory: Optimize inventory levels to minimize holding costs and avoid stockouts.
-
Leverage Debt Wisely: Use debt strategically to finance growth opportunities while maintaining a healthy debt-to-equity ratio.
-
Invest in Growth: Reinvest profits wisely in research and development, capital improvements, or acquisitions to fuel future growth.
-
Monitor Key Performance Indicators (KPIs): Regularly track important metrics related to sales, costs, and operational efficiency to identify potential areas for improvement.
-
Benchmark Against Competitors: Compare the company's ROE to industry averages and competitors to identify opportunities for improvement.
Final Conclusion
Return on Equity is more than just a formula; it's a window into a company's heart, revealing its profitability, efficiency, and overall financial health. By understanding the ROE formula, its components, and the factors influencing it, investors and business owners can make better-informed decisions. Consistent monitoring, analysis, and the implementation of strategies to improve ROE are crucial for long-term success and sustainable growth. This comprehensive guide equips you with the knowledge and tools to unlock the power of the ROE formula and make it work for you. Remember to always consider ROE in conjunction with other financial ratios and industry benchmarks for a comprehensive assessment of a company's financial health.
Latest Posts
Latest Posts
-
Alimony Payment Definition Types Requirements
Apr 04, 2025
-
Alien Insurer Definition
Apr 04, 2025
-
What Is Embedded Derivatives
Apr 04, 2025
-
What Is A Derivatives Trader
Apr 04, 2025
-
Alien Corporation Definition
Apr 04, 2025
Related Post
Thank you for visiting our website which covers about Return On Equity Roe Formula Made Easy . We hope the information provided has been useful to you. Feel free to contact us if you have any questions or need further assistance. See you next time and don't miss to bookmark.